|
We now interpret the inequality 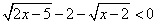 in terms of the function we have graphed. The solution
set will be all values of x for which the function Y1 has negative y-values.
Let's use TRACE to identify where these values of x are. in terms of the function we have graphed. The solution
set will be all values of x for which the function Y1 has negative y-values.
Let's use TRACE to identify where these values of x are.
Since the x-intercept has a y-value equal to 0, it is NOT part of
the solution set. The x-values to the left of 27 yield negative y-values.
The inequality 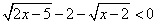 means that the graph of Y1 must lie below the x-axis. Observing the
graph, we see this is true if x is to the left of 27. We must also consider
the domain of this function, which is
means that the graph of Y1 must lie below the x-axis. Observing the
graph, we see this is true if x is to the left of 27. We must also consider
the domain of this function, which is 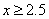 .
The inequality is not defined for values of x less than 2.5. So, the
solution set for the inequality is .
The inequality is not defined for values of x less than 2.5. So, the
solution set for the inequality is 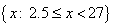 , or in
interval notation, [2.5, 27). , or in
interval notation, [2.5, 27). |
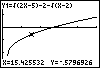
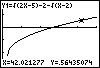
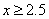 .
The inequality is not defined for values of x less than 2.5. So, the
solution set for the inequality is
.
The inequality is not defined for values of x less than 2.5. So, the
solution set for the inequality is 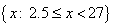 , or in
interval notation, [2.5, 27).
, or in
interval notation, [2.5, 27).