Now, perform synthetic division using the two zeros we have identified. The graph behavior suggests that x = -2 should correspond to a single factor, but x = 2/3 appears to be a repeated root. Therefore, use x = 2/3 twice in the synthetic division. The resulting quotient is the quadratic polynomial 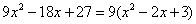 , which can be set equal to zero and solved
using the quadratic formula. The two complex solutions to this equation are , which can be set equal to zero and solved
using the quadratic formula. The two complex solutions to this equation are 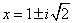 . .
Therefore, the solution set to the polynomial equation is |
|
| Copyright © 2010 Turner Educational Publishing
|
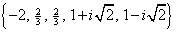 . We can also use this information to write the polynomial
function in factored form as
. We can also use this information to write the polynomial
function in factored form as 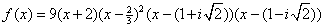 .
.